- Common Side Effects of Blood Pressure Medicine
- Why Side Effects Occur with Blood Pressure Medications
- Managing and Minimizing Side Effects
- Real-Life Examples and Patient Experiences
- Professional Advice and When to Seek Help
1. Common Side Effects of Blood Pressure Medicine
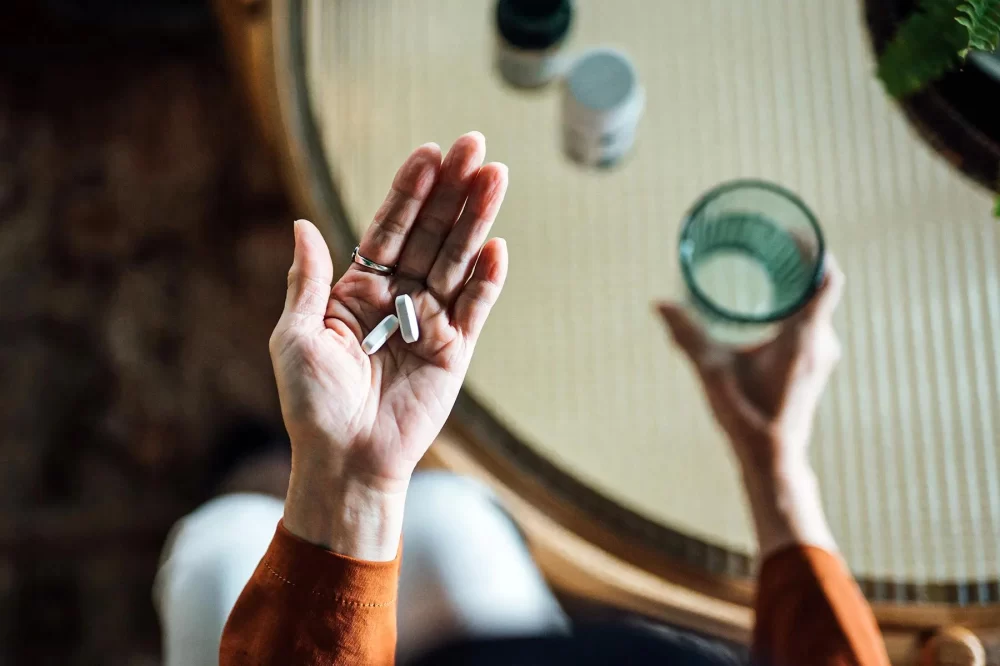
Blood pressure medicine, also known as antihypertensive medication, plays a crucial role in controlling hypertension and preventing serious cardiovascular complications. However, like all medications, these drugs can come with side effects that vary depending on the type of medication and individual patient factors.
Some of the most frequently reported side effects include dizziness, fatigue, headache, and swelling in the ankles or feet. These effects often occur as the body adjusts to the medication. For example, diuretics, commonly called water pills, may lead to increased urination and electrolyte imbalances, causing symptoms such as muscle cramps or weakness.
Beta-blockers, another common class of blood pressure medicine, can sometimes cause cold hands and feet, fatigue, or a slowed heart rate. ACE inhibitors may lead to a persistent dry cough in certain patients, which can be bothersome but typically harmless. Understanding these common side effects helps patients anticipate and manage their treatment journey better.
1.1 Detailed Insight Into Specific Side Effects
Each blood pressure medication targets different physiological mechanisms, resulting in distinct side effect profiles:
- Diuretics: May cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or increased urination frequency.
- Beta-blockers: Can induce fatigue, depression, or cold extremities due to slowed heart rate.
- ACE inhibitors: Often cause a dry cough and, rarely, elevated potassium levels.
- Calcium channel blockers: Might cause swelling (edema), headaches, or constipation.
2. Why Side Effects Occur with Blood Pressure Medications
The human body is highly complex, and medications designed to alter blood pressure do so by affecting multiple systems. For example, lowering blood pressure too quickly can cause dizziness or fainting because the brain temporarily receives less oxygenated blood. Moreover, some side effects stem from the drug’s impact on electrolyte balance or hormone regulation.
It’s also important to note that individual differences, such as age, kidney function, and the presence of other health conditions, significantly influence how someone experiences side effects. This is why blood pressure medicine is often carefully tailored and adjusted over time.
2.1 The Role of Dosage and Combination Therapy
Sometimes, side effects are more pronounced when dosages are too high or when multiple medications are combined. Many patients with hypertension require a combination of drugs to achieve optimal control, but this increases the complexity of managing side effects. Gradual dose adjustments and close monitoring are essential strategies to reduce unwanted effects while maintaining therapeutic benefit.
3. Managing and Minimizing Side Effects
Successfully managing the side effects of blood pressure medicine is key to maintaining adherence and overall health. Here are some practical steps:
3.1 Open Communication with Healthcare Providers
Patients should openly discuss any side effects with their doctors. Adjusting the medication type, dosage, or timing can often resolve problems. For example, taking medication at night might reduce daytime dizziness or fatigue.
3.2 Lifestyle Adjustments to Complement Medication
Incorporating lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can reduce the need for higher medication doses, thereby limiting side effects. Increasing hydration can help with side effects related to diuretics, and avoiding sudden position changes can minimize dizziness.
3.3 Monitoring and Support
Regular monitoring of blood pressure and symptoms is essential. Using tools like home blood pressure monitors and keeping symptom diaries can empower patients to better understand their bodies’ responses. Pharmacy professionals can also provide valuable advice and recommend products that support medication management.
4. Real-Life Examples and Patient Experiences
Consider Jane, a 58-year-old woman diagnosed with hypertension. After starting an ACE inhibitor, she experienced a persistent dry cough that disrupted her sleep. By consulting her healthcare provider and switching to a calcium channel blocker, her cough resolved, and blood pressure control improved. Jane’s story highlights the importance of personalized treatment and the role of open dialogue with medical professionals.
Similarly, Tom, a 65-year-old man on beta-blockers, reported fatigue and cold hands. His doctor adjusted the dose and recommended gentle exercise and warm gloves, which helped him manage symptoms without discontinuing medication.
Stories like these illustrate that while side effects are common, they are often manageable with the right strategies and support.
5. Professional Advice and When to Seek Help
Blood pressure medicine side effects can sometimes signal more serious problems. Patients should seek immediate medical advice if they experience symptoms such as severe swelling, chest pain, difficulty breathing, or sudden weakness. These could indicate allergic reactions or cardiovascular events requiring urgent care.
For ongoing side effects, consulting pharmacists or doctors is invaluable. Pharmacy professionals are well-positioned to offer guidance on medication interactions, over-the-counter remedies, and lifestyle tips. If you are looking for the most suitable blood pressure medicines, trusted products, or personalized advice, Pharmacy can provide comprehensive services tailored to your needs.
Ultimately, understanding common side effects of blood pressure medicine, knowing why they occur, and learning how to manage them empowers patients to take control of their health and live well with hypertension.