- Common Side Effects of Blood Sugar Medications
- Why Side Effects Occur and What Affects Them
- Managing Side Effects for Better Diabetes Care
- Real-Life Examples of Side Effects and Responses
- Professional Advice and Where to Find Help
Common Side Effects of Blood Sugar Medications
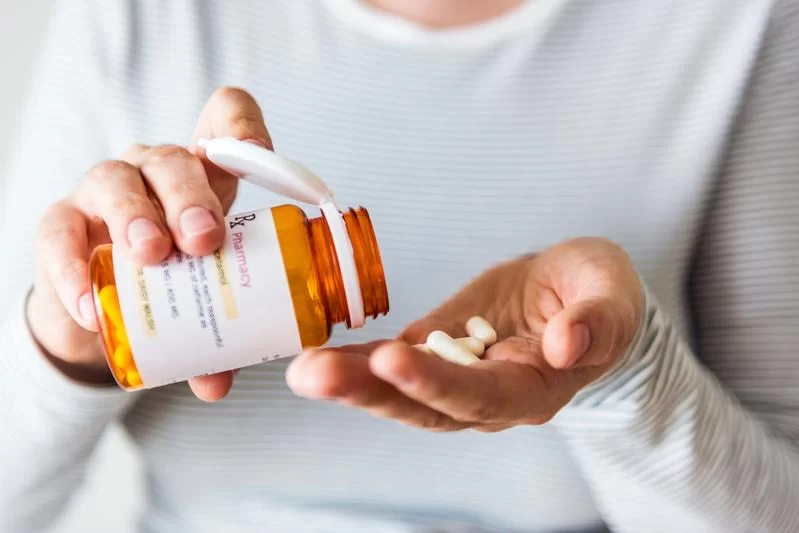
When it comes to controlling diabetes, blood sugar medications play a crucial role. However, like any medication, these drugs can come with a range of side effects. Understanding the common side effects of blood sugar medications can help patients better prepare and respond to these challenges.
One of the most frequently reported side effects is hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar. Symptoms can include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. This is often associated with insulin or sulfonylureas, which actively lower blood sugar levels.
Other typical side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, diarrhea, and stomach discomfort. Medications like metformin, widely prescribed for type 2 diabetes, are known to cause these symptoms, especially during the initial weeks of treatment.
Some blood sugar medications can also cause weight gain or fluid retention, which may affect overall health and diabetes management. For example, thiazolidinediones, a class of drugs used to improve insulin sensitivity, have been linked to these side effects.
In rare cases, patients might experience allergic reactions, skin rashes, or swelling. While these are less common, it’s important to monitor any new symptoms closely and consult healthcare professionals when needed.
Subtypes of Side Effects and Medication Classes
Blood sugar medications are diverse, and side effects often vary according to the type:
- Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues: Higher risk of hypoglycemia, weight gain.
- Metformin: Gastrointestinal upset, vitamin B12 deficiency with long-term use.
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDs): Fluid retention, weight gain, potential heart failure risk.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: Nausea, vomiting, potential pancreatitis (rare).
- SGLT2 inhibitors: Increased risk of urinary tract infections, dehydration.
Why Side Effects Occur and What Affects Them
Understanding why these side effects occur requires a look into how blood sugar medications work within the body. Each medication interacts differently with insulin production, glucose absorption, or kidney function, and these actions can trigger various bodily responses.
Individual factors play a significant role in side effect susceptibility. Age, kidney and liver function, other existing health conditions, and concurrent medications can all influence how a person reacts to blood sugar treatments.
For example, elderly patients might be more sensitive to hypoglycemia because their bodies respond less effectively to low blood sugar events. Similarly, patients with kidney impairment may accumulate certain drugs, increasing the risk of adverse effects.
Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet, alcohol consumption, and exercise routines can either exacerbate or help mitigate these side effects. It’s a delicate balance that requires personalized adjustments.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Impact
Medications’ absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (pharmacokinetics) influence side effects. For instance, metformin is processed through the kidneys, so impaired renal function can lead to increased drug levels and side effects.
Pharmacodynamics, or the drug’s effect on the body, also matters. Drugs that stimulate insulin release might cause unintended drops in blood sugar if not carefully dosed or timed with meals.
Managing Side Effects for Better Diabetes Care
Successfully managing the common side effects of blood sugar medications is essential for maintaining quality of life and effective diabetes control.
First, patients should maintain open communication with healthcare providers, reporting any new or worsening symptoms promptly. Adjustments to medication types, dosages, or timing can often reduce side effects.
Dietary changes may help mitigate gastrointestinal symptoms. For example, starting metformin with meals or splitting doses can reduce nausea or diarrhea. Staying hydrated and monitoring for signs of dehydration are important, especially with medications like SGLT2 inhibitors.
For hypoglycemia, learning to recognize early symptoms and having quick sources of glucose on hand are vital safety measures. Education about balancing medication, food intake, and physical activity can prevent dangerous lows.
Weight management strategies, including tailored exercise programs and nutritional guidance, support overall health and may counteract medication-related weight gain.
Using Technology and Support Tools
Continuous glucose monitoring systems and mobile health apps can empower patients to track blood sugar fluctuations and side effects in real-time. This data can facilitate better discussions with healthcare teams and more precise treatment plans.
Moreover, support groups and diabetes education programs provide practical advice and emotional support, helping patients cope with the challenges of treatment side effects.
Real-Life Examples of Side Effects and Responses
Consider the case of Sarah, a 52-year-old woman recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. After starting metformin, she experienced persistent stomach upset and mild diarrhea. By consulting her pharmacist and physician, she learned to take the medication with food and gradually increase the dose, which greatly improved her tolerance.
John, a 65-year-old man on insulin therapy, faced frequent hypoglycemic episodes. Through close monitoring and adjusting his insulin timing relative to meals and exercise, he reduced the occurrence of these dangerous lows significantly.
Another example is Mia, who was prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors. She noticed recurring urinary tract infections, a known side effect. Her healthcare provider switched her to an alternative medication, and with added preventive measures, her infections resolved.
These stories highlight how proactive management and patient education can turn potentially disruptive side effects into manageable aspects of diabetes care.
Professional Advice and Where to Find Help
Managing the side effects of blood sugar medications effectively requires a partnership between patients and healthcare professionals. Pharmacists are invaluable resources for advice on medication usage, side effect management, and suitable alternatives.
If you are looking for tailored recommendations or reliable products that align with your treatment plan, visiting Pharmacy can provide access to a wide range of options and expert guidance. Pharmacy offers trusted services to help you navigate your diabetes management with confidence.
Remember, never adjust or stop medications without consulting your healthcare provider. Regular check-ups and open communication are keys to safe and effective diabetes treatment.
By understanding the common side effects of blood sugar medications and employing practical management strategies, patients can achieve better control of their condition and improve their overall quality of life.